Surveillance of Total Cell Count (TCC) in a groundwater catchment
- bNovate

- Jul 24, 2025
- 3 min read

Groundwater catchment for drinking water often takes place in unconsolidated sand and gravel aquifers near rivers. These aquifers form a porous layer that allows water to flow through. It serves as a natural filter, retaining particulate and biodegradable matter, as well as microbes, through adsorption and biological processes.
If water flows through such a layer, it typically attains a high quality and can often be used directly as drinking water. It is of prime importance to monitor the raw water quality to produce drinking water of continuously high quality.
BactoSense as an early warning system
Nearby rivers can influence unconsolidated sand and gravel aquifers. The water level of the river affects the flow velocity of the water through the aquifer. Floodings can increase the flow velocity and consequently decrease the retention time of the natural filter. As a result, higher amounts of particles and microbes can reach the pumps.
The online flow cytometer BactoSense can quickly and precisely identify an increase in microbe concentration. It detects over 99% of all microbial cells and provides the results within only 20 minutes. Thanks to these measurements, actions can be taken to maintain a stable quality of drinking water.

Typical application
Measurements at a pre-warning point between the river and the pumping system, or directly within the pumping system, can monitor water quality before it enters the grid system.
BactoSense measures the total cell count (TCC), the high nucleic acid (HNA) and low nucleic acid (LNA) cell counts continuously and precisely.
TCC includes all microbial cells (intact and damaged), whereas HNA and LNA counts measure the amount of DNA, large and small, respectively, contained in each cell.
Measuring with BactoSense enables the detection of a microbe concentration increase in water within a few minutes. This early detection enables taking the proper measures if the increased microbial exposure presents a danger for the drinking water treatment as well as for the drinking water quality.
Furthermore, BactoSense enables the evaluation of the impact of the water level of a nearby river or lake on the microbial quality of the groundwater. This is a crucial parameter for predicting the quality of the water.
Field Example
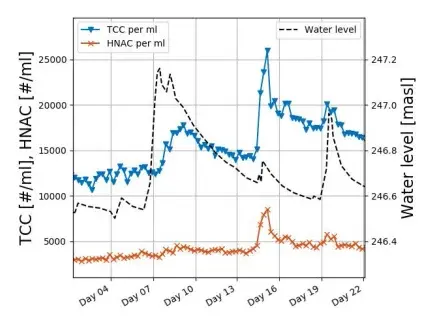
The influence of a river on a nearby groundwater catchment was investigated. Over several weeks, BactoSense continuously delivered measurements at a regular two-hour interval. The comparison of these measurements with the water level of the nearby river shows a correlation between the water level and the cell counts.
In Figure 2, it is observable that an increase in cell count follows an increase in water level of a few centimetres, a few hours later. However, the dependence of the water level on the cell count is not linear. For this reason, it is essential to measure cell counts precisely, rather than estimating them based on the water level.
Advantages of BactoSense
Flow cytometer sampling, incubation, analysis and cleaning are carried out totally automatically;
Results available 20 minutes after sampling;
Easy handling due to a safe-to-handle cartridge system. No handling of chemicals and no sample preparation necessary;
Compact instrument with a small footprint allows various applications and easy transport;
Detection of more than 99% of microbial cells;
Low operation costs;
Easy system integration thanks to multiple interfaces;
User-friendly operation and maintenance concept;
Selectable measuring interval;
Integrated colour screen shows results, graphs and hints directly;
Freely selectable gating.
Book a demo today to explore how BactoSense can help ensuring safe drinking water anywhere, anytime.










Comments